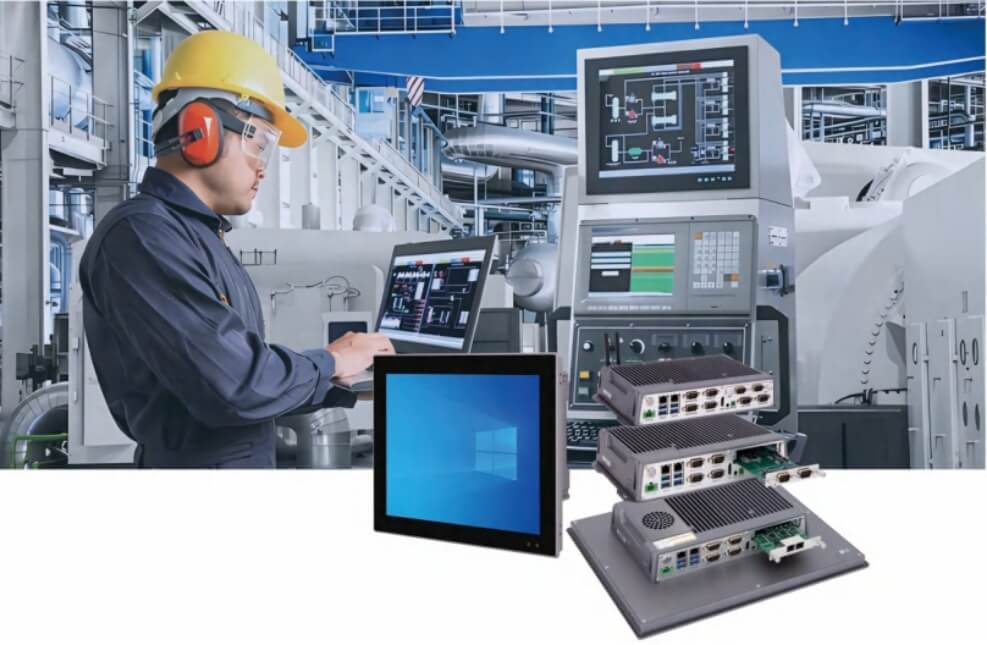
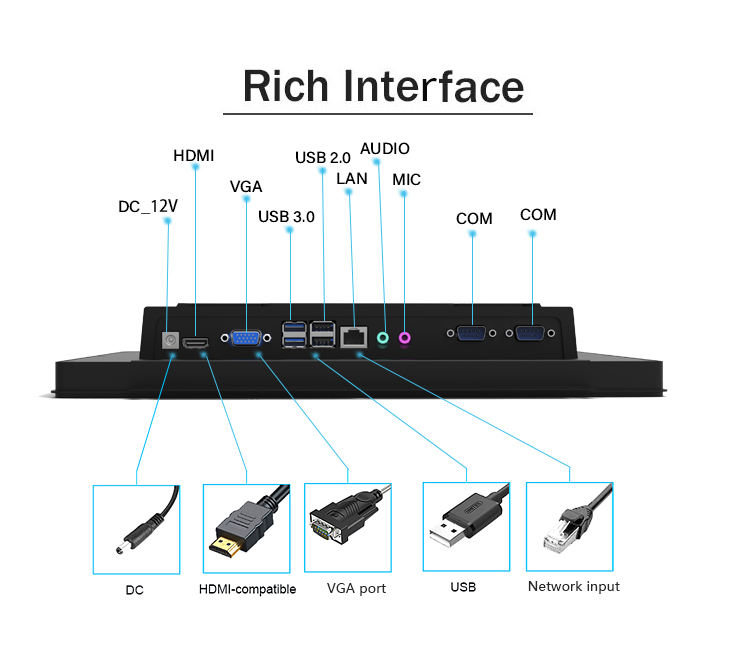
What are the connection methods between industrial computers and PLCs?
2026-01-17
Integration of Industrial PCs and PLCs:
Collaborative work and task division: The industrial PC handles advanced control and data processing, dealing with complex algorithms and decision-making logic, while the PLC focuses on real-time control, responsible for rapid response to input signals and execution of control actions.
Data exchange and secure backup: The industrial PC and PLC achieve one-to-one information exchange through data sharing. The industrial PC can send control commands to the PLC, which will update its status data to ensure coordinated operation. Finally, the industrial PC and PLC can back each other up to ensure that if one part fails, the other can continue to operate.
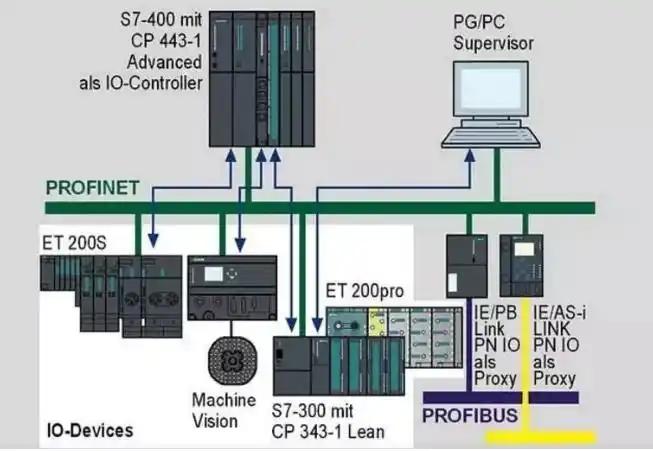
Leveraging Exceptional Efficiency and Advantages
Industrial computers offer two major advantages: data integration and management, and flexible control and programming. They can efficiently exchange data with PLCs, enabling real-time data acquisition, processing, and analysis. This is crucial for both monitoring and fault diagnosis in the production process. Industrial computers utilize high-performance CPUs, ensuring accurate and rapid data processing.
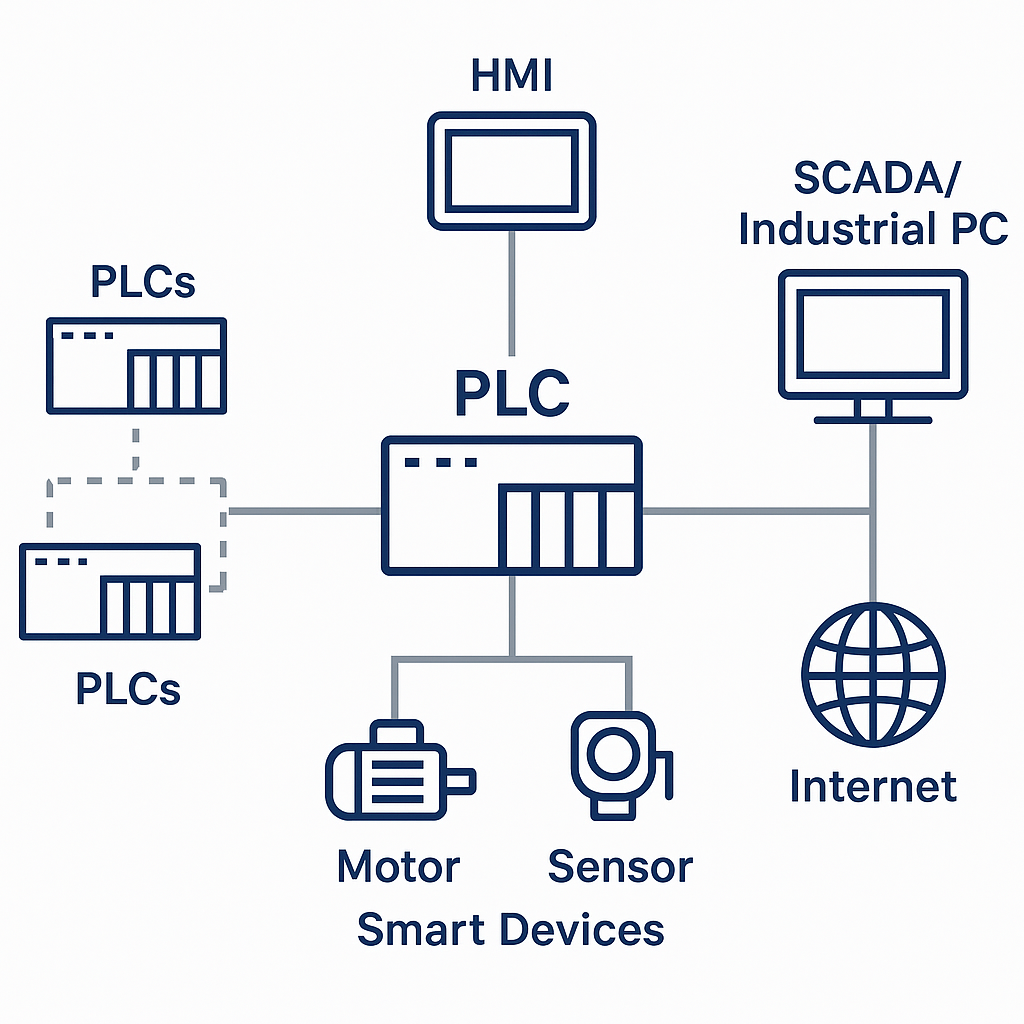
Industrial PC and PLC Connection Methods
Serial Communication: Serial communication (such as RS-232, RS-485, etc.) is one of the most basic connection methods with industrial PCs. It involves directly connecting the industrial PC and PLC through a serial port. This method is relatively simple and cost-effective, but the transmission speed is limited, making it suitable for short-distance applications with low speed requirements. Advantages: simple wiring, low cost, mature technology, and wide compatibility. Suitable for short-distance, low-to-medium speed control, such as connecting frequency converters and sensors.
Ethernet Communication:
Ethernet is currently the simplest connection method. This method improves data transmission capabilities. Through various transmission protocols (TCP/IP), industrial computers can communicate with PLCs via Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) to achieve remote monitoring and control, making the overall system more efficient, high-speed, and easy to integrate into wider networks. However, it is suitable for medium to large-scale systems requiring high-frequency data exchange or networking.
Wireless Communication:
Wireless communication technologies (such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth) provide a connection method that eliminates the need for physical cables, increasing system flexibility. Although wireless connections are not entirely stable in data transmission, they offer significant advantages in terms of eliminating the need for wiring or facilitating mobility.
Case Study of Combined Application of Industrial PCs and PLCs:
Intelligent Logistics Warehousing System:
-Description: The industrial PC is responsible for high-level control and scheduling of the logistics warehousing system, while the PLC is responsible for real-time control of various execution units, such as conveyors and stacker cranes.
The Development Trend of Industrial PC and PLC Integration:
**Hardware and Software Integration:**
Industrial PCs and PLCs will be more tightly integrated, achieving hardware and software integration, improving system stability and flexibility, and reducing integration difficulty.
**Unified Communication Standards:**
The future trend is for industrial PCs and PLCs to adopt more unified communication standards, enabling them to exchange data and work collaboratively more easily.
These trends reflect the continuous innovation in industrial automation technology, aiming to improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance system intelligence and sustainability.
Future automation systems will exhibit trends of intelligence, digitalization, sustainability, and globalization. The widespread application of intelligent decision-making and artificial intelligence technologies will make systems more autonomous and flexible, while the deep integration of the Industrial Internet will drive the digital transformation of production lines.
Collaborative work and task division: The industrial PC handles advanced control and data processing, dealing with complex algorithms and decision-making logic, while the PLC focuses on real-time control, responsible for rapid response to input signals and execution of control actions.
Data exchange and secure backup: The industrial PC and PLC achieve one-to-one information exchange through data sharing. The industrial PC can send control commands to the PLC, which will update its status data to ensure coordinated operation. Finally, the industrial PC and PLC can back each other up to ensure that if one part fails, the other can continue to operate.

Leveraging Exceptional Efficiency and Advantages
Industrial computers offer two major advantages: data integration and management, and flexible control and programming. They can efficiently exchange data with PLCs, enabling real-time data acquisition, processing, and analysis. This is crucial for both monitoring and fault diagnosis in the production process. Industrial computers utilize high-performance CPUs, ensuring accurate and rapid data processing.

Industrial PC and PLC Connection Methods
Serial Communication: Serial communication (such as RS-232, RS-485, etc.) is one of the most basic connection methods with industrial PCs. It involves directly connecting the industrial PC and PLC through a serial port. This method is relatively simple and cost-effective, but the transmission speed is limited, making it suitable for short-distance applications with low speed requirements. Advantages: simple wiring, low cost, mature technology, and wide compatibility. Suitable for short-distance, low-to-medium speed control, such as connecting frequency converters and sensors.
Ethernet Communication:
Ethernet is currently the simplest connection method. This method improves data transmission capabilities. Through various transmission protocols (TCP/IP), industrial computers can communicate with PLCs via Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) to achieve remote monitoring and control, making the overall system more efficient, high-speed, and easy to integrate into wider networks. However, it is suitable for medium to large-scale systems requiring high-frequency data exchange or networking.
Wireless Communication:
Wireless communication technologies (such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth) provide a connection method that eliminates the need for physical cables, increasing system flexibility. Although wireless connections are not entirely stable in data transmission, they offer significant advantages in terms of eliminating the need for wiring or facilitating mobility.
Case Study of Combined Application of Industrial PCs and PLCs:
Intelligent Logistics Warehousing System:
-Description: The industrial PC is responsible for high-level control and scheduling of the logistics warehousing system, while the PLC is responsible for real-time control of various execution units, such as conveyors and stacker cranes.
The Development Trend of Industrial PC and PLC Integration:
**Hardware and Software Integration:**
Industrial PCs and PLCs will be more tightly integrated, achieving hardware and software integration, improving system stability and flexibility, and reducing integration difficulty.
**Unified Communication Standards:**
The future trend is for industrial PCs and PLCs to adopt more unified communication standards, enabling them to exchange data and work collaboratively more easily.
These trends reflect the continuous innovation in industrial automation technology, aiming to improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance system intelligence and sustainability.
Future automation systems will exhibit trends of intelligence, digitalization, sustainability, and globalization. The widespread application of intelligent decision-making and artificial intelligence technologies will make systems more autonomous and flexible, while the deep integration of the Industrial Internet will drive the digital transformation of production lines.
Recommended